The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) placed the Gold King Mine and 47 other nearby sites on the Superfund cleanup list. These sites, all within the Bonita Peak Mining District, deposit an estimated 5.4 million gallons a day of heavy metal drainage into creeks within the Animas and San Juan river basins. The Superfund cleanup is a federal program that would allocate funds for the investigation and cleanup of some of America's "ticking time bombs" that would hinder human health and the environment.
 "The Bonita Peak Mining District site consists of 48 historic mines or mining-related sources where ongoing releases of metal-laden water and sediments are occurring within Mineral Creek, Cement Creek and the Upper Animas. Near Silverton, Colorado, these drainages join to form the Animas River, which is used for drinking water, recreation and agricultural purposes," according to the EPA listing. "Contaminants found in these sources and in the surface water include arsenic, cadmium, copper, manganese, zinc, lead and aluminum. These contaminants impact fisheries that are harvested for human consumption, as well as wetlands and habitat for the threatened Canada lynx."
"The Bonita Peak Mining District site consists of 48 historic mines or mining-related sources where ongoing releases of metal-laden water and sediments are occurring within Mineral Creek, Cement Creek and the Upper Animas. Near Silverton, Colorado, these drainages join to form the Animas River, which is used for drinking water, recreation and agricultural purposes," according to the EPA listing. "Contaminants found in these sources and in the surface water include arsenic, cadmium, copper, manganese, zinc, lead and aluminum. These contaminants impact fisheries that are harvested for human consumption, as well as wetlands and habitat for the threatened Canada lynx."
The Bonita Peak Mining District being added to the Superfund list is a step in the right direction that would help protect headwaters from mine drainage. Currently 40 percent of headwaters in the Western United States are affected by hard rock mining drainage. The TU-led San Juan Water Coalition has been fighting to address this issue by pushing for Good Samaritan legislation that would help clean up even more abandoned mines not addressed by the Superfund.
“Anglers and sportsmen strongly support this process,” said Trout Unlimited San Juan Mountains coordinator Ty Churchwell in a Denver Post article. “We’ll monitor the progress in the months and years to come to ensure the cleanup is done right and supports a high-quality fishery in the Animas. It’s our hope that Congress appropriates adequate funding to begin the cleanup soon."
The town of Silverton, previously  opposed to the Superfund program, now supports the listing along with local communities and law makers. “I’m hopeful that with this designation the EPA will continue to collaborate with local, tribal and state officials and work to protect the local economy, maximizing local employment opportunities where possible, and providing adequate funding to ensure the cleanup begins as quickly as possible,” said US Rep. Scott Tipton.
opposed to the Superfund program, now supports the listing along with local communities and law makers. “I’m hopeful that with this designation the EPA will continue to collaborate with local, tribal and state officials and work to protect the local economy, maximizing local employment opportunities where possible, and providing adequate funding to ensure the cleanup begins as quickly as possible,” said US Rep. Scott Tipton.
“Listing the Bonita Peak Mining District on the National Priorities List is an important step that enables EPA to secure the necessary resources to investigate and address contamination concerns of San Juan and La Plata Counties, as well as other downstream communities in New Mexico, Utah, and the Navajo Nation,” EPA regional administrator Shaun McGrath said in a statement.
“We look forward to continuing our efforts with the state of Colorado, the Bureau of Land Management, the U.S Forest Service, tribal governments and our community partners to address the impacts of acid mine drainage on the Animas River.”






 It was
It was  Projects like Stream Explorers have also helped the South Platte by teaching students about the river and how it is used for both human and aquatic needs. Learning how a city can impact the health of a river and how the river plays such a vital role to our way of life is important to teach to the next generation of river stewards.
Projects like Stream Explorers have also helped the South Platte by teaching students about the river and how it is used for both human and aquatic needs. Learning how a city can impact the health of a river and how the river plays such a vital role to our way of life is important to teach to the next generation of river stewards. Colorado Trout Unlimited, it's chapters, and volunteers helped Colorado Parks and Wildlife clip fins of Cutbow Trout as part of CPW's ongoing study of diploid vs triploid trout in Eleven Mile Reservoir.
Volunteers, along with staff from CPW helped clip over 26,000 fish in just the first day at the Mt. Shavano Fish Hatchery in Salida. Over the last two years, 97 volunteers helped clip over 148,00 fish in a six day period.
Colorado Trout Unlimited, it's chapters, and volunteers helped Colorado Parks and Wildlife clip fins of Cutbow Trout as part of CPW's ongoing study of diploid vs triploid trout in Eleven Mile Reservoir.
Volunteers, along with staff from CPW helped clip over 26,000 fish in just the first day at the Mt. Shavano Fish Hatchery in Salida. Over the last two years, 97 volunteers helped clip over 148,00 fish in a six day period. The fish used in this study are Rainbow X Cutthroat hybrid trout. Or commonly known as Cutbow trout.
The fish used in this study are Rainbow X Cutthroat hybrid trout. Or commonly known as Cutbow trout. The Western Native Trout Initiative (WNTI) has granted Colorado Trout Unlimited and the Cheyanne Mountain Chapter of Trout Unlimited $6000. Two $3,000 grants will be used to help bring public awareness to native trout and help further greenback genetic studies at Mt. Shavano Fish Hatchery. Western Native Trout Initiative is an organization dedicated to protecting native trout. They offer many different grant opportunities that provide conservation organizations with a means to realize their native trout projects.
The Western Native Trout Initiative (WNTI) has granted Colorado Trout Unlimited and the Cheyanne Mountain Chapter of Trout Unlimited $6000. Two $3,000 grants will be used to help bring public awareness to native trout and help further greenback genetic studies at Mt. Shavano Fish Hatchery. Western Native Trout Initiative is an organization dedicated to protecting native trout. They offer many different grant opportunities that provide conservation organizations with a means to realize their native trout projects.

 There was no fish mortality documented from the spill, while bug sampling by an aquatic biologist with Mountain Studies Institute indicates a still thriving population of mayfly nymphs and caddis pupa. Colorado Parks and Wildlife (CPW) had installed pens of fingerling trout in the Animas before the plume arrived- and none of those fish died either. CPW ran an electro-shocking episode after the “Spill” with the usual re-capture protocol and got essentially the same results as the year before. Actually, the survey showed a slight improvement.
There was no fish mortality documented from the spill, while bug sampling by an aquatic biologist with Mountain Studies Institute indicates a still thriving population of mayfly nymphs and caddis pupa. Colorado Parks and Wildlife (CPW) had installed pens of fingerling trout in the Animas before the plume arrived- and none of those fish died either. CPW ran an electro-shocking episode after the “Spill” with the usual re-capture protocol and got essentially the same results as the year before. Actually, the survey showed a slight improvement. The Good Samaritan Legislation would address the current pollution clean-up laws in the United States. Currently, the Clean Water Act and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, place the clean-up burden on the property owners. But in the case of these abandoned mines, the owners are long-gone. Now the clean-up falls on the shoulders of Good Samaritans like TU and other partners. However, the liabilities in the laws- requiring a project to show significant improvements for a specific period of time and makes the Good Samaritan liable for any failures in improvements- have caused a legal gridlock.
The Good Samaritan Legislation would address the current pollution clean-up laws in the United States. Currently, the Clean Water Act and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, place the clean-up burden on the property owners. But in the case of these abandoned mines, the owners are long-gone. Now the clean-up falls on the shoulders of Good Samaritans like TU and other partners. However, the liabilities in the laws- requiring a project to show significant improvements for a specific period of time and makes the Good Samaritan liable for any failures in improvements- have caused a legal gridlock.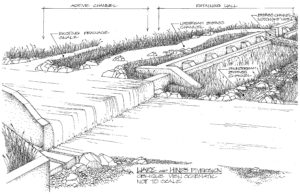 TU partnered with CPW to design and build a fish passage channel around the Ware and Hinds irrigation diversion structure on Elk Creek, a tributary to the Colorado River main-stem with its confluence at New Castle, CO. The Ware and Hinds diversion structure spans the width of the channel and presents a barrier to spawning fish moving out of the Colorado River main-stem
TU partnered with CPW to design and build a fish passage channel around the Ware and Hinds irrigation diversion structure on Elk Creek, a tributary to the Colorado River main-stem with its confluence at New Castle, CO. The Ware and Hinds diversion structure spans the width of the channel and presents a barrier to spawning fish moving out of the Colorado River main-stem The fish passage project could not have moved forward without the work from the Ferdinand-Hayden Chapter by raising $3,000 that allowed for the preliminary engineering to be completed. "This came at a critical time when I needed to finalize our design drawings," said Richard Van Gytenbeek, Colorado River Basin Outreach Coordinator. "Their contribution allowed me to pay the engineer and complete the drawings which kept the project going."
The fish passage project could not have moved forward without the work from the Ferdinand-Hayden Chapter by raising $3,000 that allowed for the preliminary engineering to be completed. "This came at a critical time when I needed to finalize our design drawings," said Richard Van Gytenbeek, Colorado River Basin Outreach Coordinator. "Their contribution allowed me to pay the engineer and complete the drawings which kept the project going." The Elk Creek passage also demonstrates the
The Elk Creek passage also demonstrates the 
