It's been a year and a few days since a spill at the Gold King Mine near Silverton released three million gallons of heavy-metal-laden, mustard yellow sludge into the Animas River. Photos of the yellow water dominated headlines all over the world. Words like "disaster" and "catastrophic" were used. While the initial spill came as a shock to most, the river was able to withstand the blow. One year after the sludge came through, the river is back to it's usual state of water quality.
 There was no fish mortality documented from the spill, while bug sampling by an aquatic biologist with Mountain Studies Institute indicates a still thriving population of mayfly nymphs and caddis pupa. Colorado Parks and Wildlife (CPW) had installed pens of fingerling trout in the Animas before the plume arrived- and none of those fish died either. CPW ran an electro-shocking episode after the “Spill” with the usual re-capture protocol and got essentially the same results as the year before. Actually, the survey showed a slight improvement.
There was no fish mortality documented from the spill, while bug sampling by an aquatic biologist with Mountain Studies Institute indicates a still thriving population of mayfly nymphs and caddis pupa. Colorado Parks and Wildlife (CPW) had installed pens of fingerling trout in the Animas before the plume arrived- and none of those fish died either. CPW ran an electro-shocking episode after the “Spill” with the usual re-capture protocol and got essentially the same results as the year before. Actually, the survey showed a slight improvement.
"This is not to diminish our concern for the Animas River and the fishery in the canyon below Silverton. This reach has been substantially impacted by three draining mines at the headwaters of Cement Creek, which flows into the Animas at Silverton," said Buck Skillen, President of the 5 Rivers Chapter of TU. "This, plus the Gold King Spill, highlights the very need for Good Samaritan Legislation for which TU is strongly advocating – so that abandoned mine cleanup projects can proceed here and elsewhere."
 Getting the river back to it's usual state was no easy task but Trout Unlimited and partners were willing to take the lead. "It’s been quite a year since the Gold King spill sent a torrent of yellow, metal-laden mine water down the Animas River in SW Colorado," said Ty Churchwell, TU San Juan Mountains Coordinator. "But long before this unfortunate event, TU was deeply embedded in the water quality conversation – and now we’ve doubled down. Our efforts to pass Good Samaritan legislation are bearing fruit in the form of a bipartisan discussion draft now working its way through the halls of Congress. We hope to see the bill formally introduced this session."
Getting the river back to it's usual state was no easy task but Trout Unlimited and partners were willing to take the lead. "It’s been quite a year since the Gold King spill sent a torrent of yellow, metal-laden mine water down the Animas River in SW Colorado," said Ty Churchwell, TU San Juan Mountains Coordinator. "But long before this unfortunate event, TU was deeply embedded in the water quality conversation – and now we’ve doubled down. Our efforts to pass Good Samaritan legislation are bearing fruit in the form of a bipartisan discussion draft now working its way through the halls of Congress. We hope to see the bill formally introduced this session."
The 5 Rivers Chapter of Colorado TU worked with Mountain Studies Institute (MSI) in Durango by taking water samples every two hours from before the plume arrived until days later. They also monitored the macro-invertebrates in the river as the disaster unfolded. The year previously, 5 Rivers Chapter had worked with MSI to do a macro-invertebrates study that served as a baseline for clean-up efforts following the spill.
Also prior to the spill in August, Trout Unlimited teamed up with other partners to form the San Juan Clean Water Coalition. The intent when forming the coalition was to produce a site-specific Good Samaritan legislation for the San Juan Mountains of Colorado. In the wake of the spill, the intentions have broadened to use the Animas as an example for the potential issues in the West.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, abandoned hard rock mines affect 40 percent of headwaters in the western United States. Just in the San Juan Mountains, slow acid drainage has led to the death of multiple rivers. "The community of Silverton, at the Animas’ headwaters, is now pursuing a Superfund listing to finally, once and for all, deal with the lingering problem of acid mine drainage (AMD) from dozens of old mining sites," said Churchwell. "The TU-led, San Juan Clean Water coalition, has grown dramatically and we’re making a real difference. In the wake of the spill, the coalition’s objectives have expanded to include a comprehensive, five-point plan to greatly improve the overall health of the watershed and the world class trout fishery in Durango"
 The Good Samaritan Legislation would address the current pollution clean-up laws in the United States. Currently, the Clean Water Act and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, place the clean-up burden on the property owners. But in the case of these abandoned mines, the owners are long-gone. Now the clean-up falls on the shoulders of Good Samaritans like TU and other partners. However, the liabilities in the laws- requiring a project to show significant improvements for a specific period of time and makes the Good Samaritan liable for any failures in improvements- have caused a legal gridlock.
The Good Samaritan Legislation would address the current pollution clean-up laws in the United States. Currently, the Clean Water Act and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, place the clean-up burden on the property owners. But in the case of these abandoned mines, the owners are long-gone. Now the clean-up falls on the shoulders of Good Samaritans like TU and other partners. However, the liabilities in the laws- requiring a project to show significant improvements for a specific period of time and makes the Good Samaritan liable for any failures in improvements- have caused a legal gridlock.
Since the Gold King Mine spill, Colorado’s Senators Michael Bennet and Cory Gardner, and Representative Scott Tipton have taken the issue to Washington where the Good Sam legislation has been moving along.
"If there are any silver linings to all of this, it’s that citizens, elected officials and communities all over the west are now aware of the massive problem of acid mine drainage, and people are paying attention. The Gold King spill was a wakeup call for the nation," said Churchwell. "Thank goodness the Animas didn’t die to make a point. In the end, there was no real ecologic ‘disaster’, as was portrayed in the media. There was no die-off of fish and our bug studies are showing excellent insect populations in the Gold Medal water in Durango. But, there is a real problem at the top of the watershed and we’re moving in the right direction. The Animas remains one of Colorado’s premier trout fisheries."






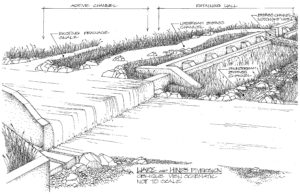 TU partnered with CPW to design and build a fish passage channel around the Ware and Hinds irrigation diversion structure on Elk Creek, a tributary to the Colorado River main-stem with its confluence at New Castle, CO. The Ware and Hinds diversion structure spans the width of the channel and presents a barrier to spawning fish moving out of the Colorado River main-stem
TU partnered with CPW to design and build a fish passage channel around the Ware and Hinds irrigation diversion structure on Elk Creek, a tributary to the Colorado River main-stem with its confluence at New Castle, CO. The Ware and Hinds diversion structure spans the width of the channel and presents a barrier to spawning fish moving out of the Colorado River main-stem The fish passage project could not have moved forward without the work from the Ferdinand-Hayden Chapter by raising $3,000 that allowed for the preliminary engineering to be completed. "This came at a critical time when I needed to finalize our design drawings," said Richard Van Gytenbeek, Colorado River Basin Outreach Coordinator. "Their contribution allowed me to pay the engineer and complete the drawings which kept the project going."
The fish passage project could not have moved forward without the work from the Ferdinand-Hayden Chapter by raising $3,000 that allowed for the preliminary engineering to be completed. "This came at a critical time when I needed to finalize our design drawings," said Richard Van Gytenbeek, Colorado River Basin Outreach Coordinator. "Their contribution allowed me to pay the engineer and complete the drawings which kept the project going." The Elk Creek passage also demonstrates the
The Elk Creek passage also demonstrates the  Groups all over the state worked together to protect our state's water quality and our trout's quality of life. CTU hired water quality expert, Ashley Rust, as a consultant to provide technical support. Her work demonstrated flaws in the data selection and analysis used for the WQCD’s proposal. TU also worked with Colorado Parks and Wildlife scientists along with other organizations including Sierra Club, Colorado Wildlife Federation, CPW and EPA.
Groups all over the state worked together to protect our state's water quality and our trout's quality of life. CTU hired water quality expert, Ashley Rust, as a consultant to provide technical support. Her work demonstrated flaws in the data selection and analysis used for the WQCD’s proposal. TU also worked with Colorado Parks and Wildlife scientists along with other organizations including Sierra Club, Colorado Wildlife Federation, CPW and EPA. "Big thanks to John Woodling, who's testimony was a turning point in the hearing," said Whiting. "To Robin (Knox) who in 5 minutes conveyed a lifetime of experience- I loved the example of all the poor fish huddling in a small pool in the Yampa to avoid the hot water in response to the Division's callous assertion that if it's too hot, fish can just swim away. Big thanks to Dennis Buechler, who very softly and meekly brought in the impacts of these decisions on small businesses."
"Big thanks to John Woodling, who's testimony was a turning point in the hearing," said Whiting. "To Robin (Knox) who in 5 minutes conveyed a lifetime of experience- I loved the example of all the poor fish huddling in a small pool in the Yampa to avoid the hot water in response to the Division's callous assertion that if it's too hot, fish can just swim away. Big thanks to Dennis Buechler, who very softly and meekly brought in the impacts of these decisions on small businesses." With many fish to be caught and much to be learned, the campers settled in to the barn that they would call home for the coming days. As the week progressed the campers gained experience in the worlds of conservation and fly fishing and made new connections with others who shared similar passions for the outdoors.
With many fish to be caught and much to be learned, the campers settled in to the barn that they would call home for the coming days. As the week progressed the campers gained experience in the worlds of conservation and fly fishing and made new connections with others who shared similar passions for the outdoors. behind genetics, and were able to see what it takes to bring back a species from endangerment. Though the camp focuses on trout conservation, the hatchery harbors nothing but native species (meaning no trout), thus enabling campers to realize that conservation goes further than just the species most popular in Colorado rivers.
behind genetics, and were able to see what it takes to bring back a species from endangerment. Though the camp focuses on trout conservation, the hatchery harbors nothing but native species (meaning no trout), thus enabling campers to realize that conservation goes further than just the species most popular in Colorado rivers. restoration project in collaboration with the Purgatoire River Anglers Chapter of CTU out of Trinidad. The Purgatoire River runs through Trinidad and has seen many restoration efforts in the past few years. Campers assisted in the removal of a fern called Russian olive- an invasive plant that consumes large amounts of water, taking it away from the river system. A day was spent using tools and chainsaws to cut down many of these large plants to better the fishery that the anglers of Trinidad value greatly.
restoration project in collaboration with the Purgatoire River Anglers Chapter of CTU out of Trinidad. The Purgatoire River runs through Trinidad and has seen many restoration efforts in the past few years. Campers assisted in the removal of a fern called Russian olive- an invasive plant that consumes large amounts of water, taking it away from the river system. A day was spent using tools and chainsaws to cut down many of these large plants to better the fishery that the anglers of Trinidad value greatly. each day, and instruction from experienced guides and fishermen, campers enjoyed testing newly tied flies on eager fish. Astoundingly, at the end of five days, every young angler, regardless of skill level was able to successfully land a fish, with dozens of healthy trout seeing the net.
each day, and instruction from experienced guides and fishermen, campers enjoyed testing newly tied flies on eager fish. Astoundingly, at the end of five days, every young angler, regardless of skill level was able to successfully land a fish, with dozens of healthy trout seeing the net.
 For this project, the chapter and partners purchased 15 RF tags that were surgically implanted into various fish in Tomichi Creek, a tributary of the Gunnison River. By attaching the RF tags to the fish in the creek, the chapter, CPW, and the partners involved could follow these trout and see what kind of movement they did and provide more information as to what causes fish to move.
For this project, the chapter and partners purchased 15 RF tags that were surgically implanted into various fish in Tomichi Creek, a tributary of the Gunnison River. By attaching the RF tags to the fish in the creek, the chapter, CPW, and the partners involved could follow these trout and see what kind of movement they did and provide more information as to what causes fish to move. "We have had a few fish travel a pretty good distance. One fish in particular, which was tagged at the Lower Tagging Location, hung out in the same area we had released him in for several weeks. Then right around the same time the runoff started picking up he bolted upstream and was last detected near the confluence of Tomichi and Cochetopa Creeks. A run of over eight miles," said Wiles. "Now there is another tagged fish that has run nearly as far. This leads us to consider that the two missing fish may be farther up the Tomichi. This has effectively expanded our search area from a five mile stretch to who knows how big. Careful what you wish for."
"We have had a few fish travel a pretty good distance. One fish in particular, which was tagged at the Lower Tagging Location, hung out in the same area we had released him in for several weeks. Then right around the same time the runoff started picking up he bolted upstream and was last detected near the confluence of Tomichi and Cochetopa Creeks. A run of over eight miles," said Wiles. "Now there is another tagged fish that has run nearly as far. This leads us to consider that the two missing fish may be farther up the Tomichi. This has effectively expanded our search area from a five mile stretch to who knows how big. Careful what you wish for." With help from a $2,500 grant from New Belgium Brewing, the chapter is expanding the project to include a website that will have a map of the Tomichi and points to where each fish is located.
With help from a $2,500 grant from New Belgium Brewing, the chapter is expanding the project to include a website that will have a map of the Tomichi and points to where each fish is located. “I wanted to get the program going locally to help students develop more awareness and appreciation for our watershed and I thought the experience might generate some interest in resource management career paths,” said Jesse Kruthaupt, Upper Gunnison Project Specialist for TU. “In addition to those benefits, understanding trout behaviors in this area will be a very useful discussion making and monitoring tool for future restoration work. TU couldn’t have done this alone, Colorado Parks and Wildlife and the Upper Gunnison River Water Conservancy District deserve a big ‘Thank You’ for helping to make this happen.”
“I wanted to get the program going locally to help students develop more awareness and appreciation for our watershed and I thought the experience might generate some interest in resource management career paths,” said Jesse Kruthaupt, Upper Gunnison Project Specialist for TU. “In addition to those benefits, understanding trout behaviors in this area will be a very useful discussion making and monitoring tool for future restoration work. TU couldn’t have done this alone, Colorado Parks and Wildlife and the Upper Gunnison River Water Conservancy District deserve a big ‘Thank You’ for helping to make this happen.” By: Ameen Hosain
By: Ameen Hosain

